The Future of Liver Healing: How Stem Cell Therapy Reverses Fatty Liver, Fibrosis & Cirrhosis
Stem Cell Therapy is a ground-breaking treatment for liver disease. Stem cell therapy not only relieves symptoms but also rebuilds the organ’s internal functionality. Stem cell therapy for liver disease offers hope to individuals who are no longer able to benefit from conventional treatments due to its unique capacity to promote regeneration and combat inflammation
This article provides an overview of what stem cells are, how they function, and the effectiveness of this treatment in liver disease.
Understanding Liver Disease: Causes, Functions, and Regeneration
The liver is a large and important organ that performs many functions, including metabolism and detoxification in the human body. Liver disease refers to a chronic condition that progressively damages the liver over time.
Many factors, including viral infection, toxic poisoning and some metabolic conditions, are the most common factors for liver disease. Naturally liver has the strongest regenerative powers, which means the liver regenerates its cells itself. But sometimes it fails due to over toxicity.
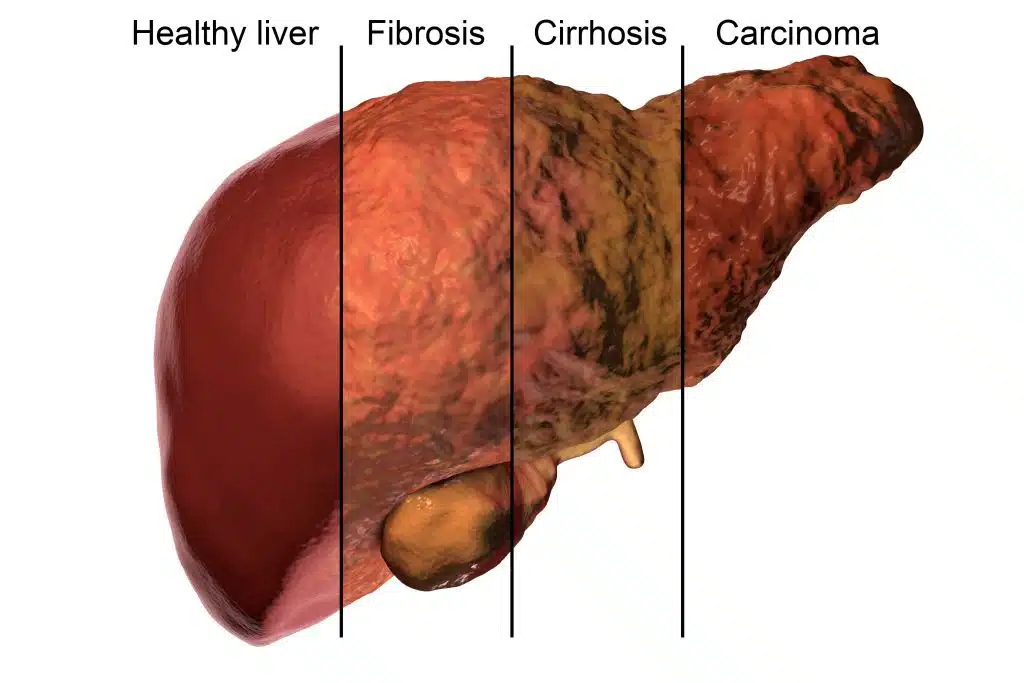
How Liver Disease Develops ?
Liver disease is responsible for 2 million deaths annually, which is 4% of all deaths worldwide. Chronic liver disease progresses through four stages.
Stage 1: Hepatitis (Inflammation of the Liver)
In the case of liver disease that develops from metabolic dysfunction. Weak metabolism leads to a stagnant liver and an underactive liver can not process and detoxify intracellular toxicity. It also impacts immune health and imbalanced immune health can cause inflammation in the body due to the lack of essential nutrients.
Stage 2: Fibrosis
Initially, continuous inflammation caused by infection such as hepatitis, can lead to fibrosis. Fibrosis is the formation of scar tissue within the liver.
Stage 3: Chirrosis
When scar tissue is extensive in the liver cells, it can block the blood flow through the liver and deteriorate the liver function day by day and shrink the liver. This condition is called Cirrhosis.
Stage 4: Liver cancer (End Stage Liver Disease/Liver Failure)
On the other hand, inflammation caused by infection is a leading cause of liver cancer. The formation of a malignant tumour within the liver is called liver cancer.
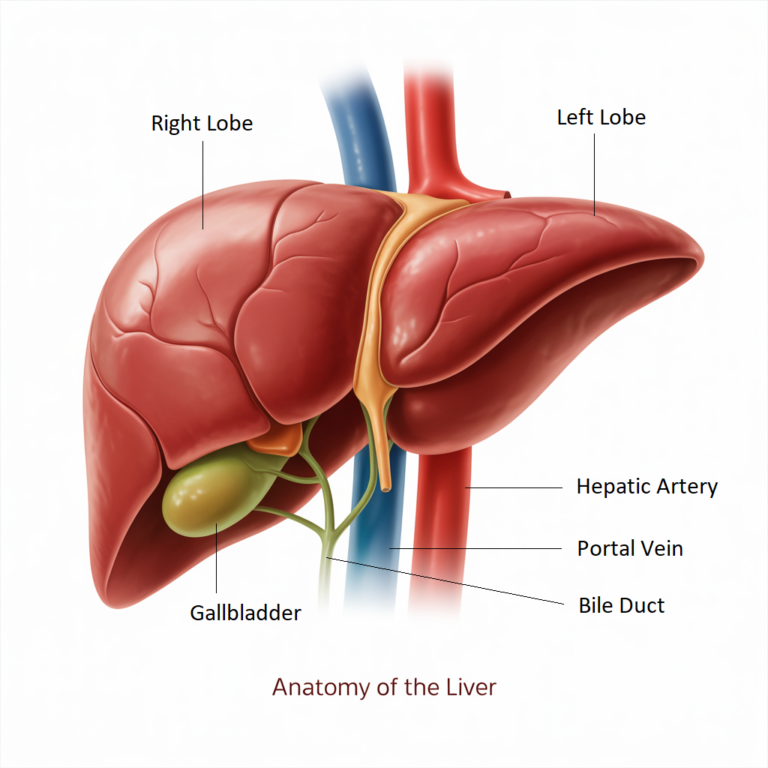
The Function Of The Liver
Detoxification and Filtration
The liver detoxifies the body by filtering blood to remove toxins, drugs, and old blood cells. It neutralizes harmful substances absorbed from the digestive tract, converting them into harmless compounds or preparing them for excretion through bile or urine.
Metabolism
The liver supports digestion and metabolism by processing nutrients such as fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. It converts them into usable energy, glucose, or storage forms like glycogen, ensuring the body maintains balanced energy levels and efficient biochemical functioning.
Bile Production
Bile, produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, is essential for fat digestion. It emulsifies dietary fats into smaller particles, enhancing nutrient absorption in the small intestine and supporting efficient elimination of waste products through the digestive tract.
Protein Synthesis
The liver synthesizes vital proteins including albumin and clotting factors that maintain blood volume, pressure, and clotting ability. These proteins are crucial for fluid balance, immune response, and preventing excessive bleeding during injury or internal tissue damage.
Hormone Secretion and Regulation
Acting as an endocrine organ, the liver produces hormones such as IGF-1, thrombopoietin, and angiotensinogen. It metabolizes and regulates hormones like thyroid and sex hormones, maintaining hormonal balance and supporting cellular growth, metabolism, and blood regulation.
Cholesterol and Hormone Production
The liver produces cholesterol and lipoproteins that transport fats throughout the body. It also regulates hormone levels by synthesizing precursors for steroid hormones and maintaining lipid metabolism crucial for cellular membrane formation and energy balance.
Nutrition Storage
The liver stores and releases essential nutrients, including glycogen, iron, and vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12. It maintains nutrient reserves, releasing them when required to sustain energy, immunity, red blood cell formation, and overall metabolic stability.
Protein Synthesis
The liver synthesizes vital proteins including albumin and clotting factors that maintain blood volume, pressure, and clotting ability. These proteins are crucial for fluid balance, immune response, and preventing excessive bleeding during injury or internal tissue damage.
Symptoms of Liver Disease
Note:
Chronic liver disease often progresses silently in its early stages, showing few or no symptoms. In some cases, it begins as acute hepatitis. Because early symptoms may resemble those of other common illnesses, liver disease often remains undiagnosed until it becomes more advanced.
Early-Stage Symptoms
Upper Abdominal Pain or Discomfort:
A dull or aching pain is commonly felt in the upper right side of the abdomen, where the liver is located. This may be due to liver inflammation or stretching of the liver capsule.
Loss of Appetite:
Reduced desire to eat, often leading to unintended weight loss and nutritional deficiencies.
Nausea or Feeling of Vomiting:
Persistent nausea or a tendency to vomit may occur due to the liver’s impaired ability to detoxify the body and process nutrients.
Fatigue and Weakness:
Constant tiredness, low energy, and generalized weakness are common as the liver fails to efficiently convert food into energy.
FAQ
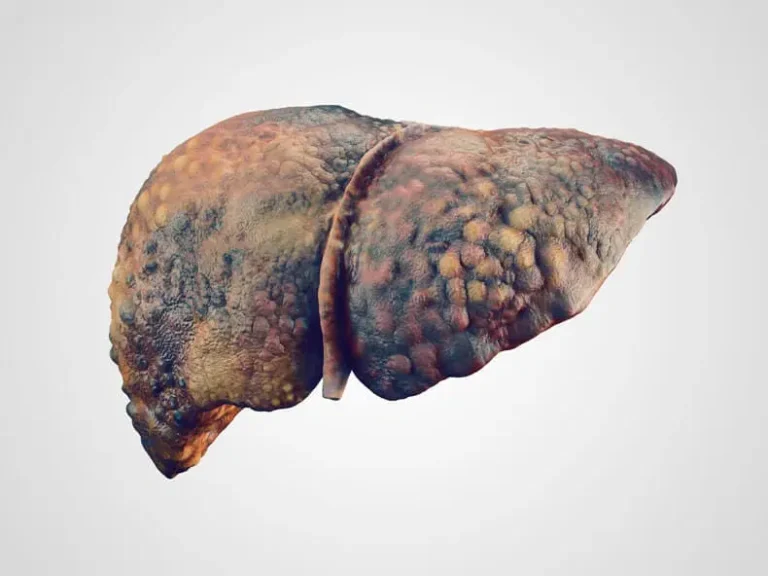
Liver damage is not always irreversible. In some cases, such as Cirrhosis, it is the most severe form of liver fibrosis (scarring). In liver cirrhosis, scar tissue and nodules replace the healthy tissue of the liver. This scar tissue or nodules prevent the liver from functioning properly and impact on blood flow in the liver.
After the severe degree of fibrosis, some nodules begin to develop on the liver. A review research study published in 2022 shows that cirrhosis becomes irreversible when nodules begin to develop within the liver.
Yes, the liver is the only internal organ in the human body that can heal and regenerate itself. Its main cells, called hepatocytes, have an incredible ability to divide and form new tissue when part of the liver is damaged or removed.
Even if up to 70% of the liver is lost due to injury, surgery, or disease, the remaining healthy cells can rapidly multiply and restore the organ to its normal size and function—often within a few weeks to a month.
However, this regeneration works best when the damage is temporary or mild. Chronic conditions like long-term alcohol use, hepatitis, or fatty liver disease can cause scarring (cirrhosis), which limits the liver’s ability to heal itself.
So yes — the liver truly can heal and regrow, but keeping it healthy is key to allowing that natural process to work effectively.
Chronic liver diseases (alcohol-associated, viral, metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease/MASLD, autoimmune) can transform into fibrosis, cirrhosis, acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), and acute liver failure (ALF). Liver transplantation remains the only option for the treatment of late stages. Inadequate donors and contraindications are the most common limitations in organ transfer. The life-saving option consideration is stem cell therapy.
From the research study, most liver disease is treated by mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSCs) from bone marrow, umbilical cord/Wharton’s jelly, or adipose tissue.
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSCs) are comparatively easy to source and expand. They exhibit immunomodulatory and tend to be immune-evasive. They allow allogeneic dosing. It’s paracrine signaling (secretome/extracellular vesicle).
According to a research study, key mechanisms include:
Anti-inflammatory and immune rebalancing mechanism: Mesenchymal stem cells modulate innate and adaptive inflammatory responses associated with hepatic inflammation and injury. This can help with liver disease.
Anti-fibrotic activity: Mesenchymal stem cells secrete factors such as microRNAs in extracellular vesicles (EVs). These factors suppress the hepatic stellate cell activation and collagen deposition. Stellate cells and collagen deposition are the core factors of fibrosis progression.
Cytoprotection (Hepatic cell protection) and Promoting New Cell Generation: Mesenchymal stem cells secrete paracrine cargo. Paracrine cargo contains growth factors, lipids, and RNAs, which promote hepatocyte survival and proliferation, increase albumin synthesis and reduce cell damage.
Limited engraftment/transdifferentiation: Almost all cells transform into liver cells by the direct replacement of hepatocytes with the help of a paracrine process.
Stem Cells for Liver Cirrhosis
Multiple clinical trials have explored the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy, with findings published across a growing number of reports.
Zhao and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis including studies published up to June 2017, encompassing 23 reports that compared mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy with conventional treatments. Their analysis indicated that MSC-based therapy is generally safe and associated with significant improvements in liver function within the first six months following treatment. The findings further suggested that a single intrahepatic arterial infusion of bone marrow–derived MSCs offers the most favorable outcomes for enhancing liver function.
Suk and colleagues conducted a phase II clinical trial investigating the efficacy of bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. MSCs were cultured from 10–20 mL of bone marrow aspirated one month prior to treatment, and patients received one or two intrahepatic arterial infusions of 5 × 10⁷ cells each. Compared with the control group, liver biopsies performed six months after MSC administration demonstrated a 25% reduction in fibrosis in the single-injection group and a 37% reduction in the double-injection group. Additionally, Child–Pugh scores in both treatment groups showed significant improvement at 12 months post-infusion, indicating enhanced liver function and clinical status.
A systematic review and meta-analysis conducted up to May 2023 evaluated the efficacy and safety of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy in liver cirrhosis using data from 11 clinical trials identified through major databases. Studies meeting the PICOS criteria were analyzed for liver function outcomes and adverse events. The pooled results revealed that MSC infusion led to significant improvements in liver function, including increased serum albumin (ALB) levels at 2 weeks, 1, 3, and 6 months, and reduced Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) scores at 1, 2, and 6 months compared with standard therapy. Hepatic arterial administration of MSCs was particularly associated with better improvements in both MELD and ALB outcomes. Importantly, no severe adverse effects were reported across studies. Overall, the findings indicate that MSC therapy is safe and effective for improving liver function and reducing complications in cirrhosis, though further high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm and standardize these results.
Another research data explores that although autologous stem cell therapy is a much-needed possibility in the treatment of liver disease, further robust clinical trials and collaborative protocols are required.
Fatty Liver (NAFLD) and Stem Cell
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) possess several beneficial properties, including immune regulation, anti-inflammatory activity, and the ability to promote tissue repair. These features have drawn interest in their potential role in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Findings from recent animal studies and early clinical research suggest that MSCs can improve liver function and reduce disease severity in NAFLD. However, challenges such as differences among MSC sources, uncertainties about long-term safety, and non-standardized treatment protocols still limit their consistent use in clinical practice.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects approximately 32% of the global population. In this condition, stem cell therapy aims to enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce oxidative stress, thereby protecting liver cells and improving overall liver function.
Hepatitis
Lin and colleagues conducted an open-label, non-blinded randomized controlled trial evaluating the therapeutic effects of allogeneic bone marrow–derived cells in patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV)–related acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). Participants received weekly infusions of 1.0–10 × 10⁵ cells/kg for four consecutive weeks and were subsequently monitored for 24 weeks. Compared with patients receiving standard medical care, those treated with cell therapy exhibited significant reductions in serum total bilirubin levels and improvements in Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) scores. Moreover, the investigators reported lower incidences of severe infections and mortality due to multiple organ failure in the MSC-treated group.
Liver Failure
A meta-analysis investigating stem cell therapy for liver failure evaluated various cell types, including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and hematopoietic stem cells, for their roles in liver regeneration. The findings indicated that MSCs hold substantial therapeutic potential in managing liver failure. When stem cell therapy was combined with standard medical treatment or plasmapheresis, patients experienced higher survival rates and lower severity scores for chronic liver failure. Notably, donor-derived MSCs demonstrated greater efficacy in improving survival outcomes compared to autologous (self-derived) MSCs.
The Stem Cells Delivery Method for Liver Disease
There are multiple ways to deliver stem cells into the body for liver disease.

